Requirements & results
Output
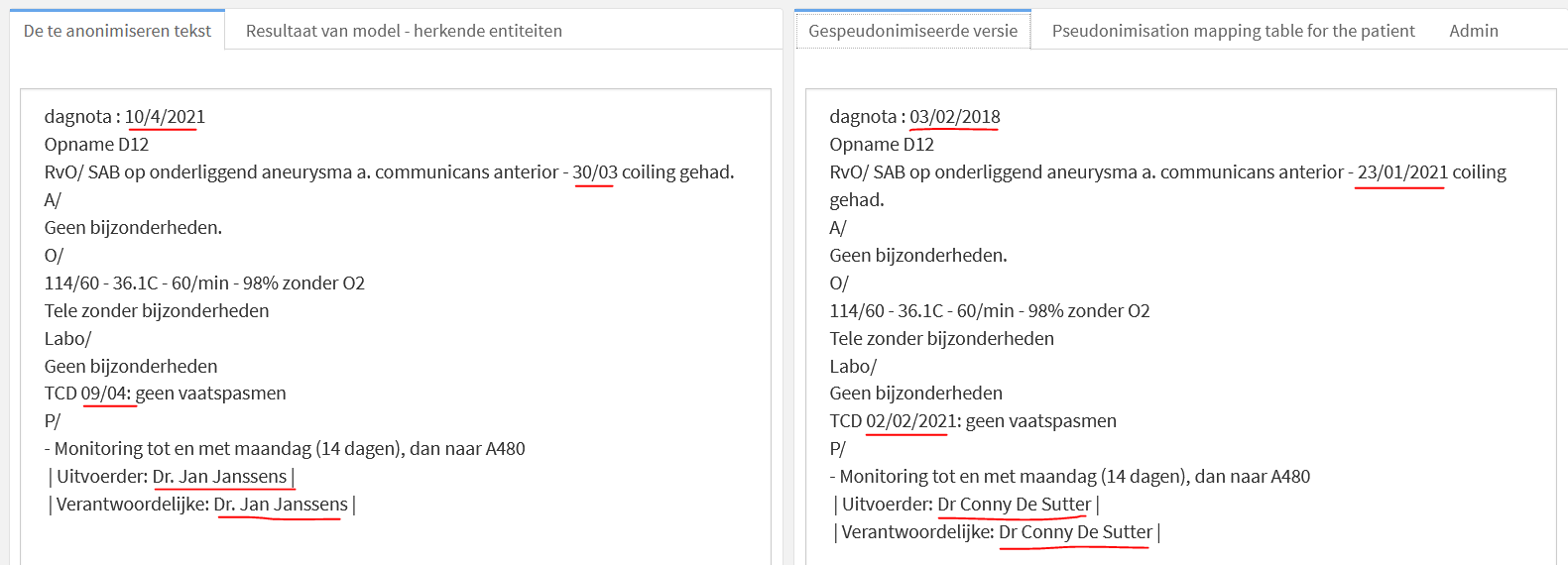
The goal of the software is the following: pseudonymized textual health records where the personally identifiable information is replaced by pseudo replacements for secondary health usage.
Requirements
In order to be able to use project blackbar, you will need a few things
- Documents with texts
- A Docker (version 24 or higher) environment which you need in order to
- start up the different webapps
- automate the anonymization and pseudonymization
- train and store the anonymization models
- host the applications and the API’s
This gets you started with the annotation so that you can provide already provide pseudonymized texts in adhoc runs to internal partners. For the automation part, you need:
- A database with documents which you would like to anonymize and pseudonymize
- Familiarity with Docker based deployments
- Familiarity with Python for testing the setup
- Optionally: a free or corporate account at Prefect to be able to monitor the anonymization progress at app.prefect.cloud if you prefer to not run Prefect locally as shown in the blackbar docs
Local server
We advise to run the software on an Linux machine (e.g. Ubuntu 22.04, Debian stable) with 4 cores and at least 32 Gb of RAM within your own datacenter. Required disk space in a normal hospital which has roughly 2.5Mio patients would be 200Gb. Such a setup is able to anonymize/pseudonymize about 4000000 text records per day.
SSL / Authentication
The webapps of project blackbar can be deployed behind an Apache webserver. Make sure you have an SSL certificate for your server and an (internal) URL where you want to host the apps and make sure you create a client for integrated OIDC authentication more info and provide the SSL certificates of the servers of the database with the documents.
Network
The following is needed network-wise
- open port 443 on the server where blackbar is running - blackbar is hosted behind Apache on port 443 (more info)
- allow access to pull the docker images from registry.datatailor.be and ghcr.io/bnosac (more info)
- allow access from the server where blackbar is running to the database containing the data
- allow access from the server where blackbar is running to the corporate authentication environment (e.g. Keycloak or Microsoft Entra ID) (more info)
- the communication between the docker images with the apps, the model building and the flows towards the setup of Inception, Minio and Prefect running on the same server are through the https port 443
- so make sure in your hosts file (e.g. /etc/hosts) the domain points to the server itself
- or allow access from the server where blackbar is running to the other servers where Inception/Minio/Prefect is running in case you decide not to run these services on the same server
- allow access to the documentation at https://bnosac.github.io/blackbar/
- optionally
- if you are using Prefect cloud and not decide to run Prefect locally: allow access from the blackbar server to Prefect cloud for monitoring the automation (whitelists needed are shown here: https://docs.prefect.io/v3/how-to-guides/cloud/troubleshoot-cloud)
- optionally allow access to pypi.org (https://pypi.org) and huggingface (https://huggingface.co/) in case you will be developing on top of the environment and will develop models and do changes to the code
Steps to get started
The following is the high-level list of steps to get you going
Basics
- Make sure you have a server with Docker which has access to internal data
- Launch the Docker container with Inception in order to annotate texts (see the section on apps and the section on training data)
- Use the cockpit app to import texts (see section apps), pre-annotate texts with an existing model from a partner hospital and automatically pseudonymize your manual annotations
Automation
- Set up the database with documents (see the database section) and test connectivity (see get-started-part1, get-started-part2, get-started-part3)
- Train a model on your own annotations (see the training section)
- Launch the anonymization and pseudonymization flows (see section automation)
- Inspect the results in the apps (see section apps)
- See behaviour of the entity detection and pseudonymization
- Validate where needed
- Export
- Optionally launch the API (see section api)
Use AI
- Use the included Generative AI apps to see how AI models work on the pseudonymized texts